Regional unemployment dynamics in Indonesia: Serial persistence, spatial dependence, and common factors
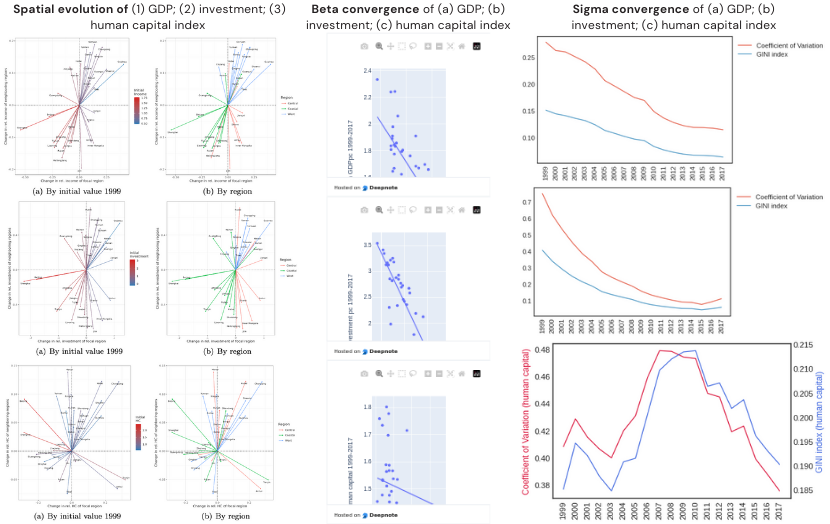
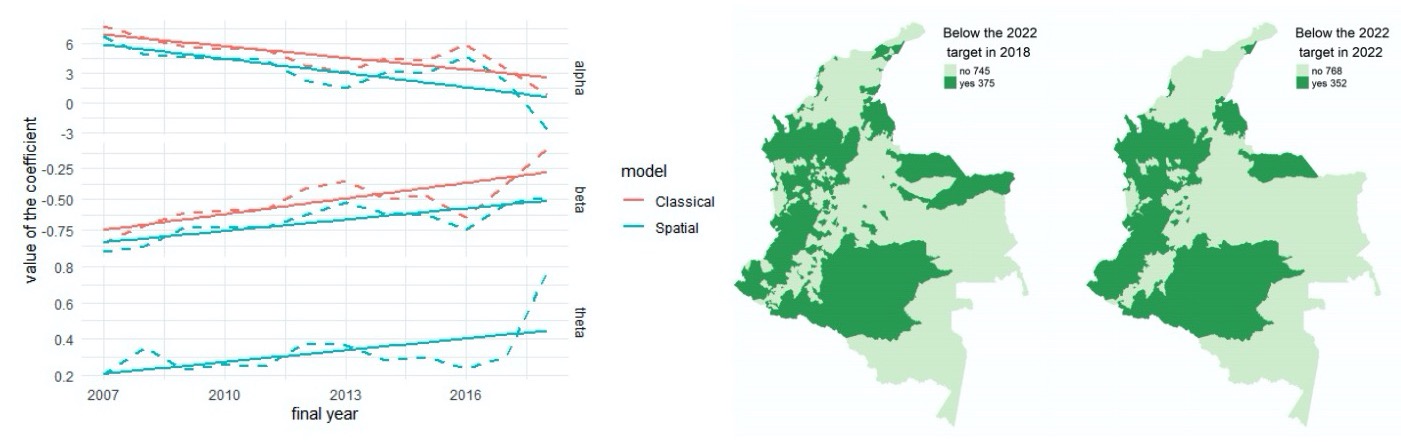
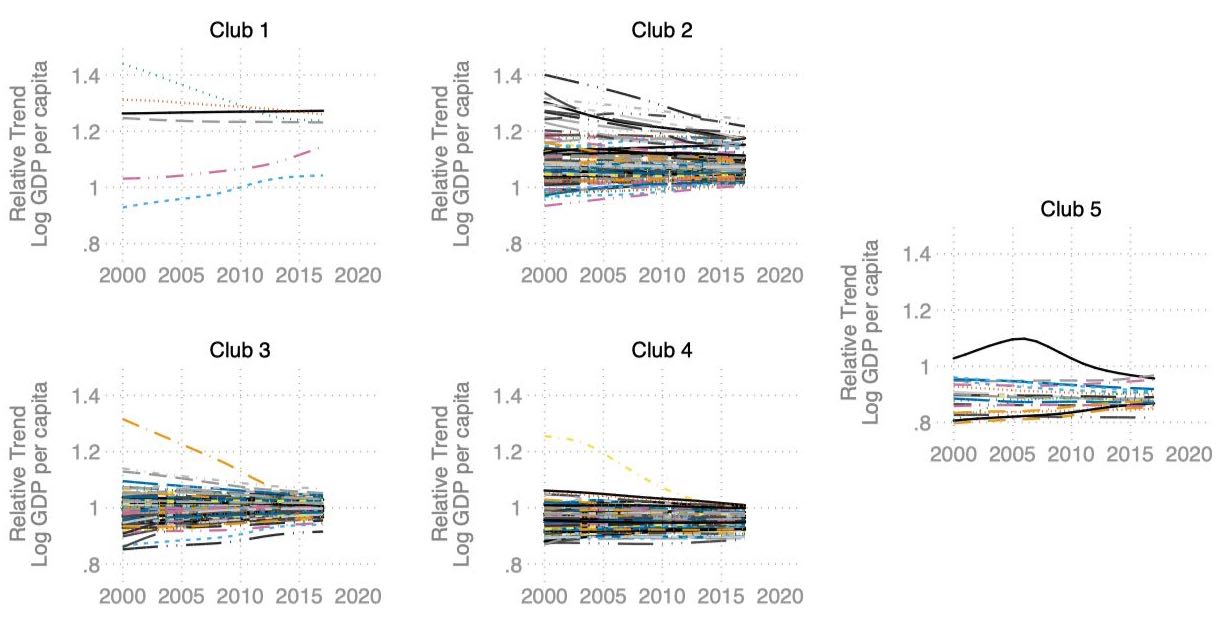
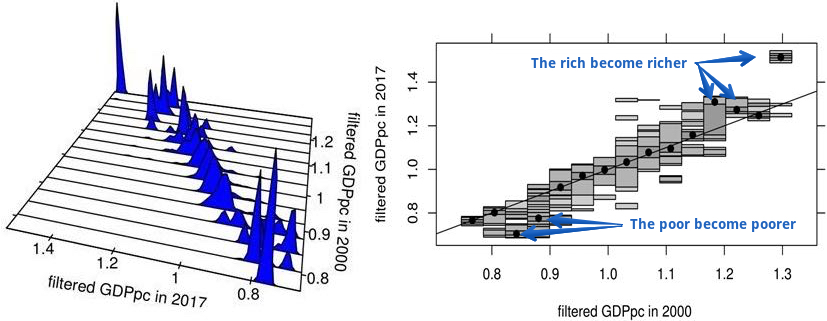
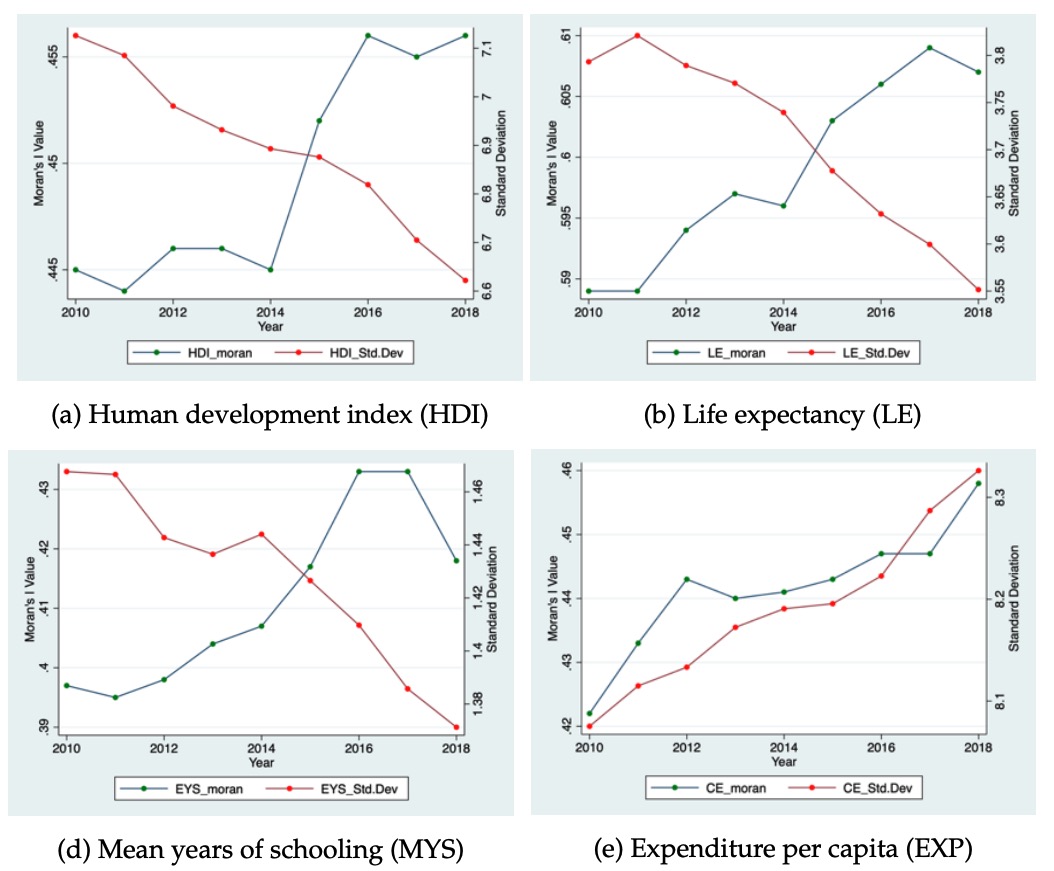
We analyze the space-time dynamics of Indonesia’s provincial unemployment by simultaneously accounting for their serial persistence, spatial dependence, and common factors. The results show that unemployment rates vary widely across provinces, but have similar patterns over time, indicating the presence of common latent factors. Using the average national unemployment rate as a proxy for common factors, the results indicate that the space-time dynamics of provincial unemployment are characterized by both significant serial persistence and spatial dependence.
Continue Reading